
16 Jan 2023
The potential to change the way we interact with the internet and with each other, leading to a more open and decentralized internet, where users have more control over their data and interactions. This can lead to greater privacy and security online, as well as new opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
The shift from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, and now to Web 3.0, represents a gradual evolution in the way we interact with the internet and with each other.
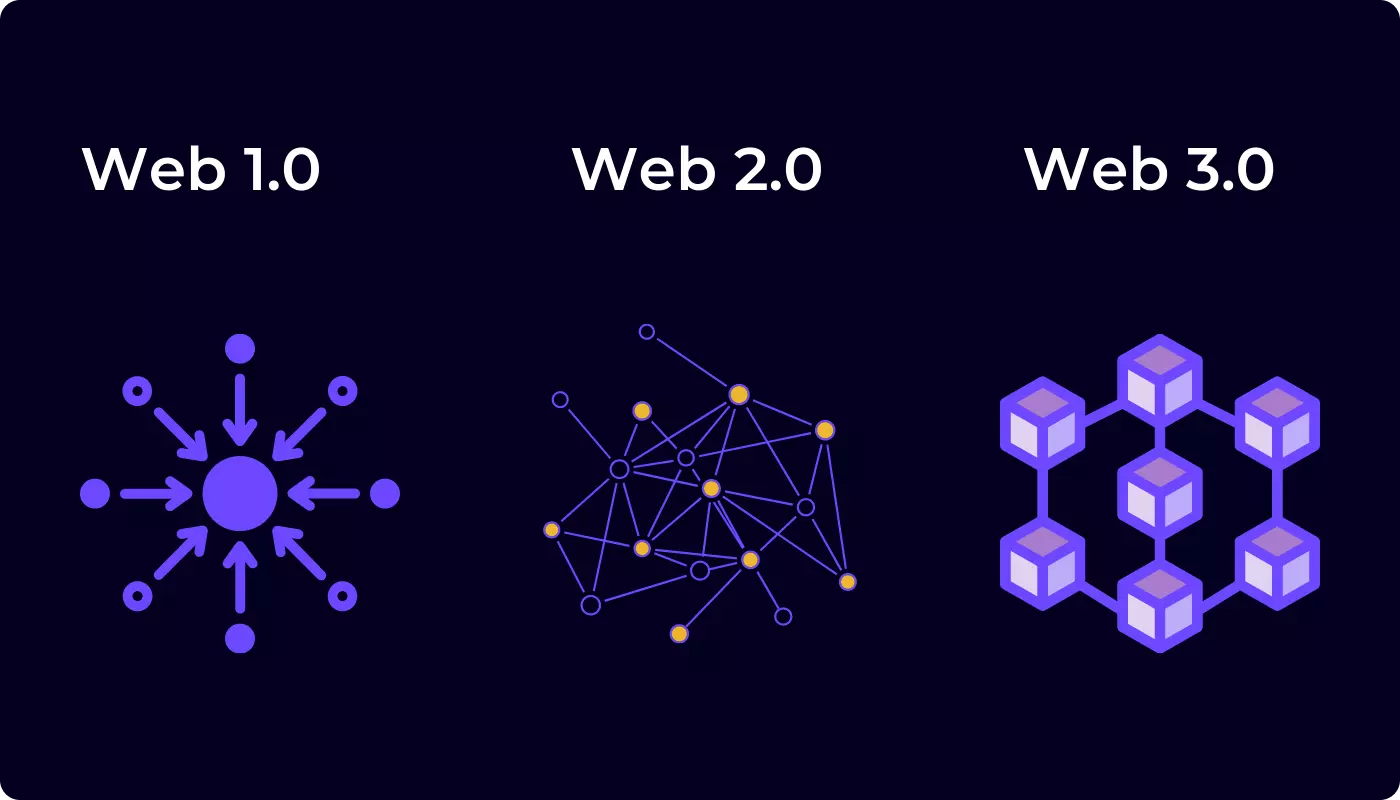
Web 1.0, also known as the "static web," was the first iteration of the internet and was primarily used for the dissemination of information. It was characterized by simple HTML pages with limited interactivity, and users could only consume content, not create or share it.
Web 2.0, also known as the "dynamic web," was a significant shift in the way we interact with the internet. It introduced interactive elements such as forums, blogs, and social media, which allowed users to create and share content. Web 2.0 also introduced the concept of "Web 2.0" applications such as Google Maps, YouTube, and Wikipedia, which were based on user-generated content and fostered collaboration.
Web 3.0, also known as the "decentralized web," is the next generation of the internet. It's built on decentralized technologies such as blockchain, peer-to-peer networks, and smart contracts. Web 3.0 allows for a more open and decentralized internet, where users have more control over their data and interactions. It also enables the creation of decentralized apps (dApps) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), which are built on blockchain technology and operate on a peer-to-peer network. These dApps and DAOs allow for a more open and transparent way of building and using applications, as well as providing new opportunities for creating and monetizing digital assets

In the traditional web (Web 1.0 and 2.0), centralized entities such as Google and Facebook have been able to gather vast amounts of personal data on their users, which they can then use for targeted advertising and other monetization purposes. The value of this data is not always clear to the user, but these centralized entities are able to monetize it through targeted advertising and other means.
In contrast, Web 3.0 is built on decentralized technologies such as blockchain, which allows for a more open and decentralized internet, where users have more control over their data and interactions. In this new web, users will have more control over their data, and they will be able to monetize it directly through the use of decentralized marketplaces and other platforms.
With Web 3.0, users will have more control over their data and will be able to monetize it directly. This can be done through tokenization of personal data, allowing users to share their data with third parties in exchange for payment. This will allow users to be compensated for the value of their data, and it will also give them more control over how their data is used.
In addition, Web 3.0 will also enable a new way of creating and monetizing digital assets, such as tokenized art and real estate, which will allow for greater liquidity and accessibility.
In Web 3.0, personal data will be tokenized, which means that it will be represented as a digital asset on a blockchain. This tokenized data can then be shared with third parties through decentralized marketplaces or other platforms.
When a user shares their data with a third party, they will receive payment in the form of cryptocurrency in exchange. The payment can be made in a number of ways, such as through a smart contract, which is a self-executing contract that automatically executes the terms of the contract when certain conditions are met. This ensures that the user is compensated for the value of their data, and it also gives them more control over how their data is used.
For example, a user might choose to share their data with a company that is developing a new product, and in exchange, they will receive payment in the form of cryptocurrency. The user will also have the ability to revoke access to their data at any time, ensuring that they retain control over their personal information.
In addition to the monetization of personal data, Web 3.0 will also enable a new way of creating and monetizing digital assets, such as tokenized art and real estate, which will allow for greater liquidity and accessibility.
Overall, Web 3.0 will enable a more transparent and equitable economy, where users will have more control over their data and will be able to monetize it directly. Additionally, it will enable the creation and monetization of tokenized assets, which can lead to greater liquidity and accessibility.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is that it is distributed and decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by a single entity. This makes it much more difficult for hackers to compromise the system, as they would need to gain control of a majority of the nodes in the network in order to make changes to the data.

In addition, blockchain technology also uses advanced cryptography to secure data, making it almost impossible for malicious actors to tamper with it. Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing an immutable record of all transactions.


 16 Jan 2023
16 Jan 2023
Copyright © 2023 Green Lava . All Rights Reserved